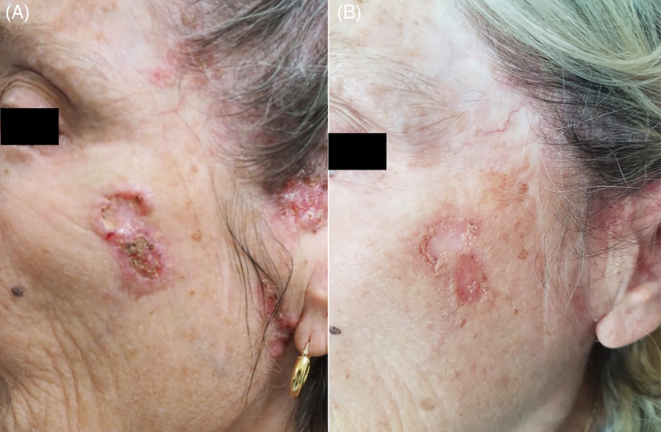
Advanced Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC) is a more serious form of the most common type of skin cancer. While it typically develops due to prolonged, unprotected sun exposure, environmental factors, lifestyle habits, certain medications, and genetics can also play a role.
If diagnosed, immediate treatment is crucial. Advanced BCC can invade surrounding tissues and even bones, becoming life-threatening if left untreated. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, or specialized medications—all tailored to your specific condition.
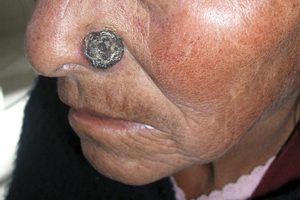
Understanding advanced progression
There’s no single definition, but advanced BCC generally refers to cases that are difficult to treat with standard methods. This could be because:
- The tumor is large, deep, or aggressive.
- Surgery isn’t an option due to proximity to vital organs (like the brain).
- Previous treatments failed, or the cancer returned.
Advanced BCC falls into two categories:
- Locally Advanced BCC – Cancer spreads to nearby tissues (most common).
- Metastatic BCC – Rarely, cancer spreads to distant organs like bones, lungs, or lymph nodes (most severe).
How does it compare to other skin cancers?
Unlike melanoma (the deadliest skin cancer), BCC starts in basal cells and grows more slowly. However, if untreated, it can cause severe damage, especially in sun-exposed areas like the face, ears, and scalp. In rare cases, it may even affect the eyes, nose, or nervous system.
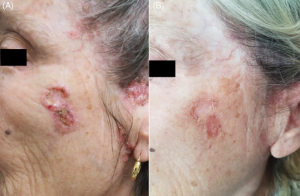
Who’s at Risk?
Factors that increase your chances include:
- A history of skin cancer.
- Genetic disorders.
- Long-term immune-suppressing medications.
- Delayed medical care.
Treatment Options
Your doctor may recommend:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor.
- Radiation: For hard-to-reach areas.
- Targeted Therapy/Drugs: If surgery isn’t possible
- Clinical Trials: For innovative treatments.
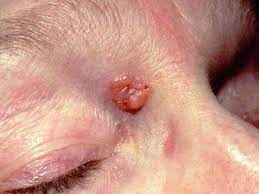
Warning Signs: When to See a Doctor
Skin cancer can affect anyone, regardless of skin tone. Watch for:
- A sore that won’t heal.
- A shiny or pearly bump.
- A brown or black lesion (in darker skin).
- A growth with rolled edges, bleeding, or itching.
Early detection saves lives—don’t ignore suspicious skin changes!