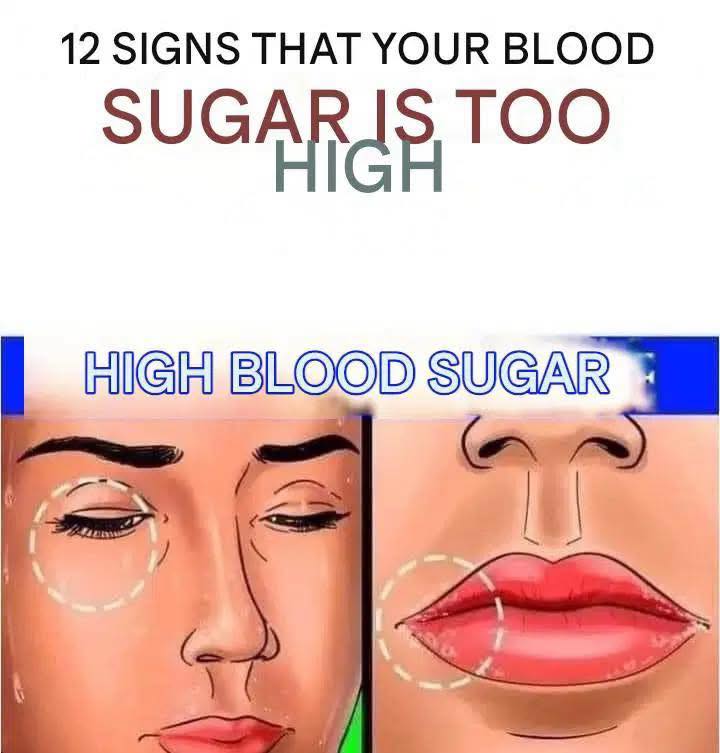
12 Signs Your Blood Sugar is Too High…Monitoring blood sugar isn’t just for people diagnosed with diabetes—it’s essential for everyone. Imbalanced blood sugar can cause a range of health issues, some of which you might already be experiencing without realizing it. In this article, we will uncover 12 signs that indicate high blood sugar, discuss the potential risks, and provide practical tips on managing your levels effectively.